In this article, Stanley Huang, MSc, Deputy Manager of Firmware Development at Raytac, shares insights on how Raytac’s modules and development kits strengthen the Zephyr ecosystem.
[Stanley Huang, New Taipei City]
When we talk about open-source platforms like Zephyr RTOS, most people immediately think of major chip manufacturers such as ST Micro, NXP, or Nordic. But to me, what truly makes Zephyr famous amongst the developer community is through modules that developers can actually touch: those they can instantly plug in and start using right away. In these terms, Raytac is one of the most underrated and important contributors in this ecosystem.
Raytac Modules Make Zephyr More Accessible
Instead of being a chip vendor, we specialize in producing high-quality, globally certified modules – especially Bluetooth and Wi-Fi modules based on Nordic chipsets, such as the AN7002Q, AN54LQ, AN54LV, MDBT53, MDBT50Q, and MDBT42Q.
All these modules are already certified with Regional RF compliances(FCC, IC, CE, KC, etc.) and the latest Bluetooth Specifications, offering developers the assurance of “plug and play” and “production-ready” solutions.
We assure that our modules have become one of the easiest platforms for Zephyr developers to test BLE functionality.
I paired Zephyr with Raytac’s MDBT50Q-DB-40 development board when I first applied Zephyr in a BLE Peripheral project . With a simple west build -b nrf52840dk_nrf52840 followed by flashing the firmware using J-Link or nRF Connect for Desktop, the BLE beacon immediately showed up on my phone. Clean, simple, noise-free, and developer-friendly – that’s Raytac’s style.
Modules play an invaluable role in product development
Many would say Raytac only makes modules and the real core is still Nordic’s SoC.
But I believe that in an open-source system like Zephyr, the hardware that helps your project runs first is that which contributes the most.
Our Zephyr-registered development kits eliminate the hassles of manual soldering, regulatory certification, and antenna design, allowing engineers to fully focus on developing applications based on Zephyr.
They can run Zephyr’s BLE peripheral, central, GATT, and HCI samples directly on the Raytac kits that act as a one-stop hardware solution.
In many ways, Raytac has pushed Zephyr’s usability a significant step forward.
Raytac Also Expands Zephyr’s Application Horizon
Many of Raytac’s modules are ultra-compact- ideal for wearables, smart sensors, and low-power beacons…etc. These are the scenarios where Zephyr excels, and Raytac’s modules provide the physical platform to enable companies to build their “dream devices".
When running Zephyr on a tiny module like the AN54LV-15(Product Link), developers will be amazed that something smaller than a piece of corn kernel can run a full RTOS, manage the BLE stack, trigger timers, drive I2C sensors, and even connect to the cloud, all by itself. This combination doesn’t just make development easier – it inspires developers to realize that: “they can build their projects using Raytac’s hardware.”
Raytac may not be the star, but we’re always ready for you
On Zephyr’s main stage, companies like Nordic, STM, and Intel take the spotlight, but Raytac plays an essential supporting role – supporting the performance from behind the scenes. We offer stable, high quality, and low-power platforms, giving every line of Zephyr code a place to run and every feature a cornerstone.
Our greatest value lies in helping developers skip antenna design and RF interference concerns – so they can jump right into the Zephyr ecosystem with ease.
Our products deliver the reliability you need and the efficiency you expect.
We invite you to explore more about how Raytac supports the Zephyr ecosystem and discover our range of development kits and modules designed for seamless integration.
Visit our Zephyr page here: https://docs.zephyrproject.org/latest/boards/raytac/index.html
Visit Zephyr’s Ecosystem Vendors page: https://www.zephyrproject.org/ecosystem-vendor-offerings/
For more information, please contact:
Raytac Contact Form: https://www.raytac.com/contact/
Raytac Sales email: sales@raytac.com
abietec Service email: service@abietec.com
Article by Firmware Deputy Manager: Stanley Huang
Edited by Business Development Manager: Tony Yin
Raytac Corporation 勁達國際電子股份有限公司 / Raytac Corporation (USA) / abietec Inc.
A Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and LoRa Module Maker/ODM & OEM Manufacturer based on
Nordic nRF54; nRF53: nRF52; nRF51; nRF7002
Semtech Specification: SX1262
Bluetooth Specification: BT6 ; BT5.4 ; BT5.3 ; BT5.2.
Wi-Fi Specification: Wi-Fi 6
LoRa Specification: LoRaWAN
All products are FCC/IC/CE/Telec/KC/RCM/SRRC/NCC/WPC/RoHS/Reach Pre-Certified.
http://www.raytac.com
https://www.raytac.com/contact/
email: sales@raytac.com
Tel: +886-2-3234-0208(TW)/+1-626-217-3139(USA)




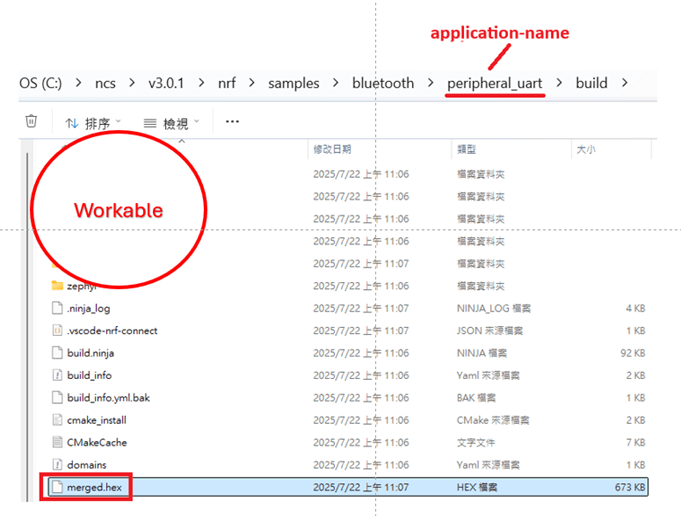
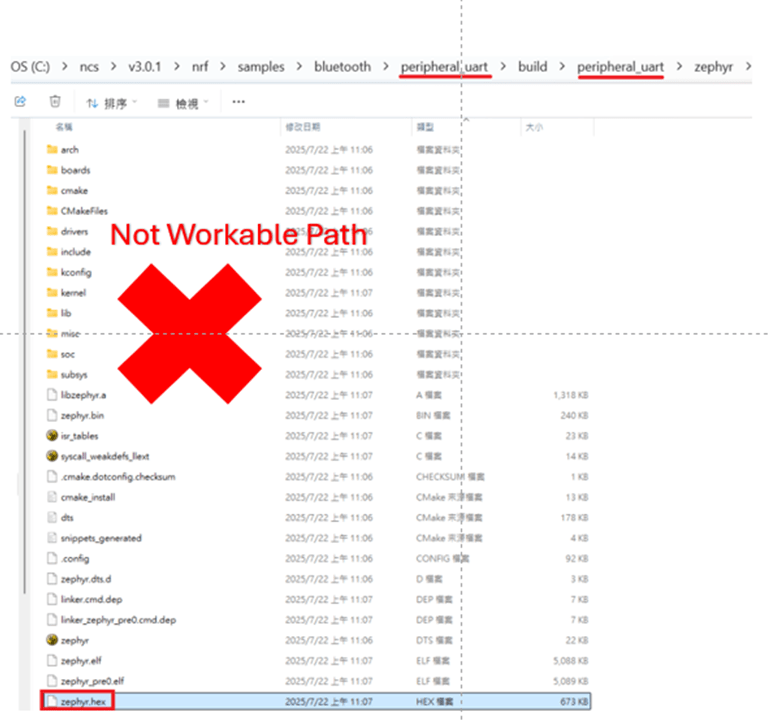









 Obviously, each and every certification has their own rules, so that’s how we’re going to do this – one by one.
Obviously, each and every certification has their own rules, so that’s how we’re going to do this – one by one.